Search
-
Which Type of Breast Health Screening is Right for You?
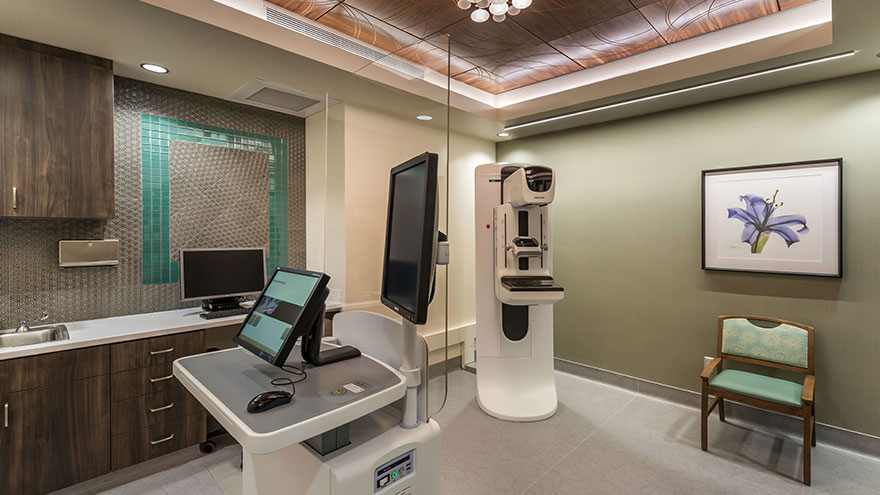
Reviewed by Dr. Colleen O'Kelly-Priddy, MD, FACS, breast surgical oncologist at Renown Women's Health. In the United States, breast cancer is the most common cancer among women, with approximately 1 in 8 women developing breast cancer during their lives, reports the American Cancer Society. These statistics can be a little startling; however, when it comes to taking charge of your health, early detection is key. The National Breast Cancer Foundation, Inc. reports that when breast cancer is caught in its earliest, localized stages, the 5-year relative survival rate is 99%. The earlier breast cancer is found, the more treatment options are available and better survival rates are seen. New technology and evolving screening guidelines are crucial for women to understand and choose the right screening method for their specific needs. The most common types of screenings available today are: 2-D Mammography 3-D Mammography Whole Breast Ultrasound What is the Difference Between 2-D Mammography and 3-D Mammography? 2-D Mammography: In a standard 2-D mammogram, the tech takes X-rays of the breast, compressing it top-to-bottom and side-to-side, providing a 2-dimensional view in each direction. These pictures can show the radiologist if there are abnormalities you might not be able to feel. 3-D Mammography: In 3-D mammography, or “tomosynthesis,” the process is largely the same, but more images are taken, and it takes a few seconds longer. This kind of exam provides a more detailed view because it reduces the overlap of tissues that can take place in a standard 2-D mammogram. Using 3-D mammography, radiologists can detect 41 percent more cancers and reduce the number of callbacks for additional imaging. This improvement in technology is great for both patients and their care providers. Renown uses 3-D mammography because it produces better images of the breast, enabling doctors to more accurately diagnose and reduce false positives, especially in women with dense breast tissue.
Read More About Which Type of Breast Health Screening is Right for You?
-
Life-Saving Mammograms: Real Women, Real Stories
Renown patients share how early mammogram screenings transformed their lives. From detecting cancer in its earliest stages to celebrating successful recoveries, these stories emphasize the importance of regular screenings and taking charge of breast health. Early detection is key! Book your mammogram with Renown Women's Health and prioritize your breast health. Book Your Mammogram Angie T. "I'm so grateful that the cancer was caught early. Those screening exams are so important and actually saved my life. I encourage women to make time to get their mammograms like their lives depend on it; because in some cases, it does." Amber S. “I was diagnosed with breast cancer at the age of 40 with what would have been my first annual screening exam. This was caught in the earliest stage possible with many of my findings being only pre-cancerous. Because of early detection, I did not have to have chemotherapy or radiation as part of my treatment plan.” Monica T. “I truly believe the yearly 20-minute diagnostic mammogram screening and findings saved me from allowing cancer to take control of my future.” Jes H. “It is because of breast cancer risk assessment testing that I was able to identify my risk for breast cancer early. I am so very thankful that I am going to be able to watch my children grow up.” Melissa P. “A yearly mammogram can save your life! A routine mammogram found my cancer at stage 1 when it was easily treated! “ Sharon C. “Despite having minimal family history, I was diagnosed at 47. Renown provided exceptional care for both my double mastectomy and reconstruction. For me, knowing my body was the key, when I felt like something was not right, I followed up with my physician and made sure I was doing everything to minimize my risk.” Jamie V. “My annual mammograms have detected 3 lumps in the last 10 years. Two were benign and one was cancer. My annual mammogram and then my ultrasound saved my life by detecting my cancer in its earlier stages.”
Read More About Life-Saving Mammograms: Real Women, Real Stories
-
Why Mammograms Are Vital for Early Breast Cancer Detection | Renown Health
Breast cancer affects 1 in 8 women in the U.S. each year, making early detection crucial in improving the chances of successful treatment. Early Detection for Treatment and Peace of Mind Mammograms are noninvasive X-rays used to detect cancer and other abnormalities in the breast. They are the most effective screening tool for detecting breast cancer early, allowing for timely treatment before the disease can spread and helping to improve treatment outcomes. To help guide you through the mammogram process, we spoke with Elizabeth Kang, PA-C, at Renown Breast Surgery Care to equip you with expert knowledge on what to expect and why screening is so important. How Accurate are Mammograms? 3-D mammography technology at Renown Breast Health Center can detect 41% more cancers and reduce the number of false-positive results compared to plain film mammography. Benefits of 3-D mammography include: Providing better, clearer images, with higher diagnostic accuracy Allowing radiologists to see more abnormalities in the breast Helping doctors spot more cancers and avoid false positives, especially if you have dense breast tissue Reduced callback rates for findings on screening Mammogram Screening and Breast Exam Recommendations Renown Women's Health recommends the following breast exam guidelines: Age 18-39: Consult your primary care provider for a Risk Assessment and start breast exams at age 25. Age 40+: Get your annual mammograms. Family history: Begin screening 10 years before your youngest family member's age at diagnosis. For example, start at age 35 if a family member was diagnosed at 45. Self-awareness: Be familiar with the look and feel of your breasts and report any changes to your care provider. Age 75+: Continue annual mammograms if life expectancy exceeds five to seven years. What screenings are available for women with breast implants? Women with breast implants can and should still receive mammograms, and it’s essential to have these screenings done by an experienced team. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider and mammogram technicians about your implants, as they may recommend special techniques or steps to detect abnormalities and ensure accurate results.
Read More About Why Mammograms Are Vital for Early Breast Cancer Detection | Renown Health
-
What it's Really Like to Have a Mammogram
Have you found yourself avoiding scheduling a mammogram because it sounds uncomfortable and maybe a little scary? Many people feel this way but knowing what to expect can help ease your worries. Follow along for a reassuring step-by-step guide on getting a mammogram from Melissa Dahir, Community Relations Liaison at Renown Health. Getting a mammogram is important to me because my mom is a Stage 3, double mastectomy breast cancer survivor. I began receiving annual breast health screenings at an early age, in addition to performing monthly self-exams. So far, all my appointments have gone well, and I hope that sharing my experience will encourage you to schedule this important screening today! Scheduling the Appointment Scheduling my appointment was very easy. I contacted the scheduling team for help with booking multiple appointments and they were very helpful in finding just the time I needed.
-
Ladies! Get Screened for Breast Cancer
Early detection is a significant piece of the breast cancer puzzle. Susan Cox, Renown Health Senior Director of Cancer Operations, discusses what you need to watch for and how the latest technology can help detect potential cancer sooner. When should women start getting breast exams? It depends on risk factors: Average-risk women: Most medical organizations recommend the first mammogram between 40 and 44. Higher-risk women: Dependent on their high risk, which will dictate when they start screening, but generally around the age of 30 and not before 25 years old.
-
Do Mammograms Hurt? 4 Myths Debunked
Mammograms are an effective means for early detection of breast cancer. Still, many women shy away from them for fear of pain or discomfort. Let us debunk a few mammogram myths that will remove your worries and encourage proactive breast health. Reviewed by Dr. Colleen O'Kelly-Priddy, MD, FACS, breast surgical oncologist at Renown Women's Health. Myth 1: Mammograms Are Painful Reality: Although some women experience discomfort during a mammogram, most say it is not painful. Breast compression, which is important to get a clear image, can cause a sensation of pressure, but this lasts for a few seconds. Let your technician know how much pressure you can handle so you're not uncomfortable. Myth 2: Discomfort Persists Long After the Procedure Reality: The sensation of pressure developed through the compression process diminishes quickly after the procedure. Most women go about their day afterward without experiencing any residual pain.
-
7 Symptoms of Breast Cancer in Young Women
Cancer can develop at any age, and that’s why the experts at Renown are ready to help you stay ahead of breast cancer, especially if you're in your 20s or 30s. We're talking about early detection, signs to be aware of, and why being proactive is a big deal. Studies show there has been an increase in breast cancer in younger women. Although breast cancer is rare in women under 40, when it occurs, it tends to be aggressive. The tricky part? Many young women don't think it can happen to them, so they don't check for the signs as often as they should. Reviewed by Dr. Colleen O'Kelly-Priddy, MD, FACS, breast surgical oncologist at Renown Women's Health. Early Signs and Symptoms New or Different Lump in the Breast: A lump is probably the most well-known symptom. Breast cancer is usually painless and firm, but it can also be soft. If you find a new lump, don't panic, but don't ignore it either. Changes in Breast Size or Shape: Have you noticed that one breast looks a little different? Whether it's swelling, shrinking, bulging, dimpling, or seems off, it's worth mentioning to your doctor. Skin Changes: If the skin on your breast starts to thicken or turn red, it's time to pay attention. If your skin starts looking like an orange peel (thickened, with prominent pores), that warrants evaluation. Nipple Discharge: Spontaneous drainage coming from your nipple that isn't breast milk—especially if it's clear or bloody—should be checked out. Nipple Changes: If your nipple starts to invert, flatten, or look different, call your doctor. Breast Pain: Continuous pain in your breast or nipple that isn't linked to your menstrual cycle is another symptom to note. However, breast pain is very common and is only rarely a sign of cancer, so don’t panic. Swelling or Lumps in the Armpit: When it spreads, breast cancer usually first goes to the lymph nodes in the armpit, so swelling or lumps under your arm should be on your radar.
-
Guide to Cancer Screenings
One of the most crucial aspects of maintaining health and wellness is staying proactive about regular cancer screenings. Early cancer detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. The multidisciplinary care team at the William N. Pennington Cancer Institute at Renown Health provides compassionate care and support to the community for early detection and diagnoses. This comprehensive guide outlines the various cancer screenings available for breast, colorectal, lung, cervical, prostate and skin cancer. Breast Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Mammograms are recommended starting age 40 for those considered at average risk for breast cancer. Women with a family history or other risk factors should discuss appropriate screening options with their healthcare provider. Women under 40 with a family history should discuss risk factors with a healthcare provider. Screening Methods Mammogram: This provides an X-ray of the breast and can detect tumors that are not yet palpable. Breast MRI: This type of scan is recommended for women at high risk for breast cancer due to genetic factors or family history. Screening Breast Ultrasound: This scan can help in identifying masses in denser breast tissue that might not be visible on mammogram. It is recommended in addition to a mammogram for patients at a higher risk for breast cancer. What to Expect During a mammogram, the breast is compressed between two plates to capture X-ray images. Some pressure or discomfort may be felt, but the procedure is brief and critical for early detection. Colorectal Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Adults aged 45 to 75 should undergo regular colorectal screenings. Some adults under 45 may need to be screened earlier depending on family history or other genetic risks. Those over 75 should consult with their healthcare provider to determine if continued screening is necessary. Screening Methods Colonoscopy: This procedure uses a flexible tube with a camera to examine the entire colon. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): A non-invasive test that detects hidden blood in the stool. CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy): Uses Computed tomography (CT) imaging to provide detailed views of the colon. What to Expect A colonoscopy can detect changes or abnormalities in the large intestine (colon) and rectum. Screening is usually advised every ten years, but if you are at risk, screening may be recommended every 3 to 5 years after your initial colonoscopy. Colonoscopy preparation includes bowel cleansing the day before and sedation during the procedure. FIT is a simple at-home test requiring no special preparation. Lung Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Adults aged 50 to 80 with a significant smoking history (20 pack years or more) and who currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. Screening Methods Low-dose Computed Tomography (LDCT): A CT scan with low radiation doses to create detailed images of the lungs. What to Expect LDCT is a non-invasive scan that requires you to hold your breath for a few seconds. Cervical Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Women aged 21 to 65 should undergo regular screenings. Women aged 21 to 29 should have a Pap test every three years. Women aged 30 to 65 should have a Pap test and HPV test every five years, or a Pap test alone every three years. Screening Methods Pap Test (sometimes called a Pap Smear): Collects cells from the cervix to detect precancers. HPV Test: Identifies high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) types that can cause cervical cancer. What to Expect The Pap test involves collecting cells from the cervix using a small brush. Some discomfort may be felt, but the procedure is brief and crucial for early detection. Prostate Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Men aged 50 and older should discuss screening options with their healthcare provider. Men at higher risk (African American men and those with a family history of prostate cancer or are a BRCA2 gene carrier) should begin discussing screenings at age 40. Screening Methods Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures PSA levels in the blood. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A physical examination where the provider feels the prostate through the rectum to detect abnormalities. What to Expect The PSA test is a simple blood test. The DRE may cause slight discomfort but is quick and essential for early detection. Skin Cancer Screening Who Should Get Screened? Anyone with a suspicious lesion or abnormal area on their skin. Individuals with more than 50 moles or dysplastic moles. Those with a personal history of melanoma or history of other skin cancers. Those who have more than one member of immediate family with a history of cancers (melanoma, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer) or a family member who was diagnosed with melanoma before they were 50 years old. Positive gene testing for BRACA2, Lynch syndrome genes (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 or EPCAM). Screening Methods Skin Exam: A visual examination by your provider to check for unusual moles, birthmarks, or other skin changes. Biopsy: Removal of a small sample of skin for testing if an abnormal area is identified. What to Expect A skin exam is non-invasive and visual. A biopsy involves minor discomfort and local anesthesia if needed. Expert Advice Although the cadence of these skin screenings may or may not be annual, as one's age increases, the risk of many cancers rises. Everyone benefits from attentive sun protection, including avoiding direct sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. by seeking shade and wearing hats, clothing and sunscreen. When purchasing sunscreen, look for SPF 50, UVA/UVB broad spectrum. Questions to Discuss with Your Healthcare Provider What is my risk level for different types of cancer? Which screening tests do you recommend for me and why? What are the potential risks and benefits of each test? How often should I get screened? What steps to follow if a test result is abnormal? Importance of Cancer Screenings Regular cancer screenings are vital for maintaining your health and catching cancer early, when it is most treatable. Renown Health is dedicated to guiding you through the process and providing the highest quality of care. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screenings for your specific needs and to take proactive steps toward a healthier future.
-
Optimizing Mammogram Screenings: A Genetic Approach to a Personalized Screening Schedule
© Arthon Meekodong via Canva.com Breast cancer screening has long been a cornerstone of women's healthcare. With 1 in 8 women diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime1, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has developed screening recommendations to help detect early-stage cancer. Notably in 2023, the USPSTF revised the recommended age for biennial mammogram screenings for women with average risk to start at age 40 instead of 502, estimated to result in 19% more lives being saved3 by starting screening earlier. While initiating screening at an earlier age offers advantages to a wide demographic, concerns about the potential of over-screening prompted research into the feasibility of identifying women with lower breast cancer risk who could safely delay mammograms. While guidelines address high-risk individuals, a notable gap exists in providing recommendations tailored to those at lower risk. To gain insight into a patient's risk level, physicians are able to utilize genetic testing to understand an individual's genetic makeup, providing precise insights into their predisposition to various health conditions, including breast cancer. Armed with this genetic information, healthcare providers could craft tailored screening strategies that align with an individual’s specific risk profile. This genetic risk-based approach underscores the value of genetics in individualizing the onset of screening to help avoid over-screening and its associated costs. Surprisingly, genetic information is not currently being widely utilized to identify women at risk of breast cancer or other diseases in clinical practice, despite its potential to make a significant positive impact for patients. A recent retrospective analysis of 25,591 women from the Healthy Nevada Project4 sheds light on the potential benefits of this genetic risk-based approach. The study classified 2,338 (9.1%) of these women as having a low genetic risk for breast cancer. What's remarkable is that these women exhibited a significantly lower and later onset of breast cancer compared to their average or high-risk counterparts. This finding suggests that it might be safe for low-risk women to delay mammogram screening by 5 to 10 years without compromising their health.