What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
By: Tori Bowlin
February 13, 2024

Dr. Carilyn Hoffman with Renown's Women's Health explains the symptoms, causes and treatments of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) (also referred to as Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD)), a prevalent condition among women of reproductive age that influences hormonal balance, metabolism and fertility.
Make an appointment with Renown Women's Health
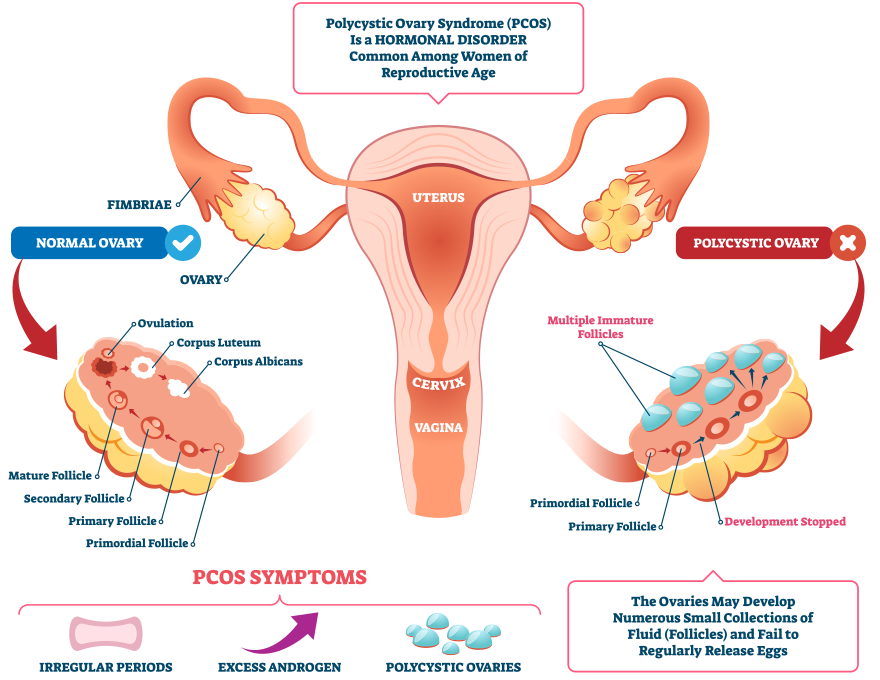
PCOS Defined
PCOS is a constellation of symptoms characterized by two of the three criteria: multiple small cysts on the ovaries visible via ultrasound, irregular periods and signs of hyperandrogenism. Other symptoms include infertility, insulin resistance, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from woman to woman, but some of the most common include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: This is often one of the first signs of PCOS. Women may experience fewer than nine periods a year, more than 35 days between periods, frequent spotting, and/or abnormally heavy periods.
- Excess androgen levels: High levels of male hormones may result in physical signs such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic ovaries: Enlarged ovaries containing numerous small cysts can be detected via ultrasound.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors may play a role:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of PCOS increases the risk.
- Insulin resistance: High insulin levels might increase androgen production, causing difficulty with ovulation.
- Obesity: Women with elevated BMI’s are more likely to have PCOS, although 20% of women with PCOS are not obese.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Dr. Hoffman outlines that diagnosing PCOS requires a medical history review, a physical exam, blood work and an ultrasound to evaluate the ovaries. Treatment options can range from lifestyle modifications, like diet and exercise and weight loss, to medications for menstrual regulation, fertility assistance, and rarely surgery.
Lifestyle Changes
- A healthy lifestyle is a cornerstone of managing PCOS. Regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and weight management can help reduce symptoms and the risk of long-term health issues. In overweight patients, weight loss as little as 5% has been shown to improve symptoms of PCOS.
Medication
- Medications may include hormonal contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles, anti-androgens to reduce hair growth and acne, and Metformin to address insulin resistance.
Fertility Treatment
- For women with PCOS who are trying to conceive, ovulation induction with clomiphene or letrozole is sometimes necessary. Sometimes a referral to a reproductive endocrinologist and infertility specialist is needed for more advanced technologies like IVF.
Health Implications
PCOS is not just about cystic ovaries or irregular periods; it can have profound implications on a woman's overall health. Women with PCOS are at an increased risk for several conditions, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and endometrial cancer.
Renown Women's Health
Expert PCOS and Reproductive Health Support at Renown Women's Health.

